Thailand Facts Updated January 12, 2012
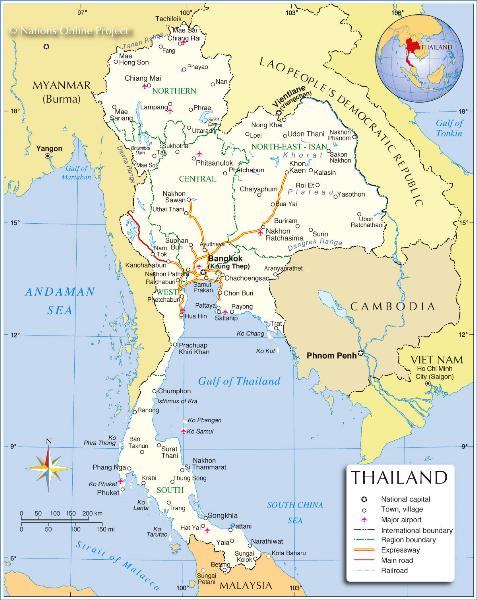
Thailand is situated in South-East Asia, covering an area of nearly 513,115 square kilometres. It is roughly the size of France. It shares land borders with Myanmar (Burma) in the north and west, the Andaman Sea in the west, Laos in the north and north-east, Cambodia and the Gulf of Thailand in the east, and Malaysia in the south.
The shape of the country is similar to the profile of an elephant with a long trunk stretching down the peninsular. At school, students are taught that their country resembles the shape of an ancient axe with the peninsular being the handle.
Thailand Geography :
Thailand covers a land area of 513,115 square kilometres (198,114 square miles), extends about 1,620 kilometres (1,007 miles) from north to south and 750 kilometres (482 miles) at its widest point from east to west, or approximately the same size as France, with a coastline of approximately 2,700 kilometres (1,143 miles) on the Gulf of Thailand and 865 kilometres (537 miles) along the Indian Ocean.
Lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
Highest point: Doi Inthanon 2,576 m
Geographic coordinates: 15 00 N, 100 00 E
Natural resources: tin, rubber, natural gas, tungsten, tantalum, timber, lead, fish, gypsum, lignite, fluorite
Climate: The climate is sub-tropical with long hours of sunshine and high humidity. There are three seasons. The hot season lasts from March to June. The rainy season, from July to October. The cool season from November to February. Average low temperature is 20c and high temperature is 37c. The geographic and climatic conditions make the country suitable for the cultivation of a wide range of tropical and semi-tropical agricultural crops.
Land use: arable land: 34%, permanent crops: 6%, permanent pastures: 2%, forests and woodland: 26%, other: 32%.
Irrigated land: 49,000 sq km
Thailand is divided into four geographical regions : Central Thailand (including Bangkok), Northern Thailand, Northeastern Thailand, and Southern Thailand. The country has also an Eastern Region which is often included into the Central Region.
Thai People :
Population 65,905,410
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2008 est.)
Age Structure:
0-14 years: 20.8% (male 7,009,845/female 6,691,470)
15-64 years: 70.5% (male 22,977,945/female 23,512,538)
65 years and over: 8.7% (male 2,594,387/female 3,119,225) (2009 est.)
Median Age:
total: 33.3 years
male: 32.4 years
female: 34.2 years (2008 est.)
Birth Rate:
13.57 births/1,000 population (2008 est.)
Death Rate:
7.17 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.)
Infant mortality rate 20.48 deaths/1,000 live births ; total fertility rate 1.64 born/woman (higher in provinces, lower in Bangkok).
Infant mortality rate:
Definition Field info displayed for all countries in alpha order Comparison to the rest of the world
total: 17.63 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 18.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 16.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
Definition Field info displayed for all countries in alpha order Comparison to the rest of the world
total population: 73.1 years
male: 70.77 years
female: 75.55 years (2009 est.)
Total fertility rate:
Definition Field info displayed for all countries in alpha order Comparison to the rest of the world
1.65 children born/woman (2009 est.)
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate:
Definition Field info displayed for all countries in alpha order Comparison to the rest of the world
1.4% (2007 est.)
HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS:
Definition Field info displayed for all countries in alpha order Comparison to the rest of the world
610,000 (2007 est.)
HIV/AIDS – deaths:
Definition Field info displayed for all countries in alpha order Comparison to the rest of the world
30,000 (2007 est.)
Major infectious diseases:
Definition Field info displayed for all countries in alpha order
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, and malaria
animal contact disease: rabies
water contact disease: leptospirosis
note: highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
Ethnic groups : Thai 75%, Chinese 14%, other 11%
Religions : Buddhist 94.6%, Muslim 4.6%, Christian 0.7%, other 0.1% (2000 census)
Languages : Thai, English (secondary language of the elite), ethnic and regional dialects( Lao,Kmer…ect.)
Literacy :
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 92.6%
male: 94.9%
female: 90.5% (2000 census)
Thailand Government :
The conventional long name of the country : Kingdom of Thailand. Short name : Thailand, formerly named Siam.
Thailand has a constitutional monarchy. King Bhumibol Adulyadej is head of state. Bangkok is the capital of Thailand. The country has 76 provinces.
chief of state: King PHUMIPHON Adunyadet or (BHUMIBOL Adulyadej) (since 9 June 1946)
head of government: Prime Minister ABHISIT Wetchachiwa, also spelled ABHISIT Vejjajiva (since 17 December 2008); Deputy Prime Minister KORBSAK Saphawasu, also spelled KORBSAK Sabhavasu (since 22 December 2008); Deputy Prime Minister SANAN Kachornprasat, also spelled SANAN Kachornparsart (since 7 February 2008); Deputy Prime Minister SUTHEP Thueaksuban, also spelled SUTHEP Thaugsuban (since 22 December 2008)
cabinet: Council of Ministers
note: there is also a Privy Council
elections: monarch is hereditary; according to 2007 constitution, prime minister is designated from among members of House of Representatives; following national elections for House of Representatives, leader of party that could organize a majority coalition usually was appointed prime minister by king; prime minister is limited to two 4-year terms.
Legislative Branch:bicameral National Assembly or Rathasapha consisted of the Senate or Wuthisapha (150 seats; 76 members elected by popular vote representing 76 provinces, 74 appointed by judges and independent government bodies; all serve six-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Sapha Phuthaen Ratsadon (480 seats; 400 members elected from 157 multi-seat constituencies and 80 elected on proportional party-list basis of 10 per eight zones or groupings of provinces; all serve four-year terms)
elections: Senate – last held on 2 March 2008 (next to be held in March 2014); House of Representatives – last election held on 23 December 2007 (next to be held in December 2011)
election results: Senate – percent of vote by party – NA; seats by party – NA; House of Representatives – percent of vote by party – NA; seats by party – PPP 233, DP 164, TNP 34, Motherland 24, Middle Way 11, Unity 9, Royalist People’s 5
note: 74 senators were appointed on 19 February 2008 by a seven-member committee headed by the chief of the Constitutional Court; 76 senators were elected on 2 March 2008; elections to the Senate are non-partisan; registered political party members are disqualified from being senato
Judiciary : Supreme Court or Sandika (judges appointed by H.M. the King)
Political Parties and Leaders:
Chat Thai Phattana Party or CP (Thai Nation Development Party) [CHUMPON Silpa-archa]; Democrat Party or DP (Prachathipat Party) [ABHISIT Wetchachiwa, also spelled ABHISIT Vejjajiva]; Motherland Party (Phuea Phaendin Party) [CHANCHAI Chairungrueang]; Phuea Thai Party (For Thais Party) or PTP [YONGYUT Wichaidit]; Phumchai (Bhumjai) Thai Party or BJT (Thai Pride) [CHAVARAT Charnvirakul]; Royalist People’s Party (Pracharaj) [SANOH Thienthong]; Ruam Jai Thai Party (Thai Unity Party) [WANNARAT Channukul]
Economy :
With a well-developed infrastructure, a free-enterprise economy, and generally pro-investment policies, Thailand appears to have fully recovered from the 1997-98 Asian Financial Crisis. The country was one of East Asia’s best performers from 2002-04. Boosted by strong export growth, the Thai economy grew 4.5% in 2007. Bangkok has pursued preferential trade agreements with a variety of partners in an effort to boost exports and to maintain high growth. By 2007, the tourism sector had largely recovered from the major 2004 tsunami. Following the military coup in September 2006, investment and consumer confidence stagnated due to the uncertain political climate that lasted through the December 2007 elections. Foreign investor sentiment was further tempered by a 30% reserve requirement on capital inflows instituted in December 2006, and discussion of amending Thailand’s rules governing foreign-owned businesses. Economic growth in 2007 was due almost entirely to robust export performance – despite the pressure of an appreciating currency. Exports have performed at record levels, rising nearly 17% in 2006 and 12% in 2007. Export-oriented manufacturing – in particular automobile production – and farm output are driving these gains.
Communications :
There are many Thai language T.V. stations. English-language programs are also widely available through cable TV (including BBC, CNN, NSBC etc.)
Mobile phone use is widespread, with approximately half the populations owing a mobile phone. There are more mobile phones than fixed line phones.
Internet access is available throughout the country. Cities and towns in Thailand have Internet-Cafes with cheap rate of access (less than 1 dollar per hour usually). Broadband services are also available and are now being heavily promoted.
general assessment: high quality system, especially in urban areas like Bangkok
domestic: fixed line system provided by both a government owned and commercial provider; wireless service expanding rapidly and outpacing fixed lines
international: country code – 66; connected to major submarine cable systems providing links throughout Asia, Australia, Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations – 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean, 1 Pacific Ocean)
Trans-National Issues:
separatist violence in Thailand’s predominantly Muslim southern provinces prompt border closures and controls with Malaysia to stem terrorist activities; Southeast Asian states have enhanced border surveillance to check the spread of avian flu; talks continue on completion of demarcation with Laos but disputes remain over several islands in the Mekong River; despite continuing border committee talks, Thailand must deal with Karen and other ethnic rebels, refugees, and illegal cross-border activities, and as of 2006, over 116,000 Karen, Hmong, and other refugees and asylum seekers from Burma; Cambodia and Thailand dispute sections of historic boundary with missing boundary markers; Cambodia claims Thai encroachments into Cambodian territory and obstructing access to Preah Vihear temple ruins awarded to Cambodia by ICJ decision in 1962; Thailand is studying the feasibility of jointly constructing the Hatgyi Dam on the Salween river near the border with Burma; in 2004, international environmentalist pressure prompted China to halt construction of 13 dams on the Salween River that flows through China, Burma, and Thailand
Illicit Drugs:
a minor producer of opium, heroin, and marijuana; transit point for illicit heroin en route to the international drug market from Burma and Laos; eradication efforts have reduced the area of cannabis cultivation and shifted some production to neighboring countries; opium poppy cultivation has been reduced by eradication efforts; also a drug money-laundering center; minor role in methamphetamine production for regional consumption; major consumer of methamphetamine since the 1990s despite a series of government crackdowns
For more interesting facts about Thailand such as: Did you know the King of Thailand is an American citizen, check out And you thought you knew about Thailand.
Sources : National Statistical Office, Bank of Thailand ; NESDB ; CIA World Factbook